Electric vehicles: An approaching confluence of opportunity and demand
The market for electric vehicles is gaining ground around the world, and the upheavals that this is creating will have unavoidable consequences for the Thai auto industry, but despite this, consumer interest in electric vehicles within the country lags the changes being seen overseas. In light of this discrepancy, in November 2021, Krungsri Research carried out a survey of consumer opinions on electric vehicles, looking in particular at demand, obstacles to growth, and consumer behavior, with the research also exploring ways in which players in the sector could adapt better to future market conditions.
The research reveals that those who had already bought an electric vehicle were motivated by their lower operating costs, their reduced environmental impact, and their use of more advanced technology. However, on the downside, the lack of charging stations, their low range, slow charging speeds, and high-cost relative to traditional internal combustion engine-powered vehicles were all commonly cited obstacles to greater acceptance of electric vehicles in the domestic auto market. Over 80% of respondents planned to purchase a vehicle within the next 5 years, and there are high interests in battery electric vehicles. Demand for EVs is likely to pick up through 2022 and 2023, though during this period, sales will be concentrated at mid to upper price points. However, from 2024 onwards, demand growth will both accelerate and mutate, with the center of gravity in the market shifting to smaller, more affordable vehicles, and so with time, the market will see changes in terms of both target consumer groups and their preferred vehicle types. In addition, because EVs are still a novel product, brand loyalty remains weak and fluid.
Beyond these changes to the market, operators will have to face rising competition and fundamental alterations to the structure of the industry, and to meet these challenges, auto manufacturers and players in associated parts of the economy will need to look for fresh paths through this new industrial landscape. This might involve, for example, revamping the range of goods and services on offer, connecting with new consumer groups, developing new types of business activities, or partnering with players both inside and external to the auto industry, all of which will help to build competitiveness and provide players with the confidence to face the future from a position of strength.
Since the invention of the first automobile in 1886, through the development of the auto production line 30 years later and the dramatic effect this had on making cars a mass-market product that gradually became available worldwide, and continuing up to the present day, the 130-odd-year history of powered land transport has been marked by the continuous development of the engines that bring vehicles to life. Progress with this has been instrumental in allowing the car to become one of the central features of modern life worldwide, but recently a profound shift has occurred, and vehicles have transitioned from being absolutely dependent on the internal combustion engine (ICE) as the primary source of motion to seeing a growing place for the use of electric motors and with this, the increasing development of the electric vehicle (EV) segment. These now take several distinct forms, including hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), which use a combination of power from ICEs and electric motors, plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), which are similar to HEVs but offer the option of also being charged directly from a plug-in source of electricity, and battery electric vehicles (BEVs), which have no petrol engine and are powered entirely by an electric motor that has to be plugged in to be charged.
However, although they are widely regarded as a recent invention, electric vehicles were initially developed in the 1880s, and so their first appearance was contemporaneous with ICE-powered vehicles. Over the next 30 years, these early EVs were nearly as popular as petrol-driven vehicles but their low speed and short range became increasingly problematic as the development of road networks in Europe and the USA encouraged the public to travel further by car. As such, interest in EVs waned and in their place, ICE-powered autos achieved complete dominance, and it was not until nearly a century later that the further development of EVs reignited consumer interest.
Despite the Covid-19 crisis, sales of EVs continue to reach new highs, and this is then feeding into the development of new ecosystems within the global EV market
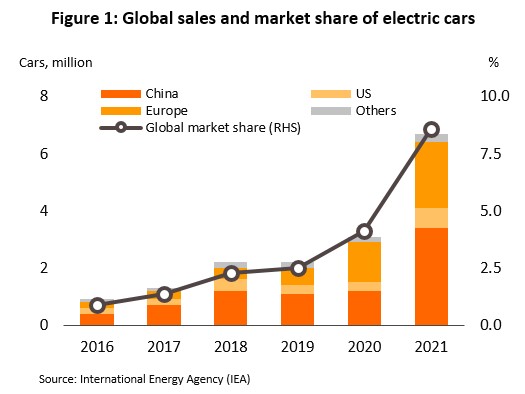
A recent report by the International Energy Agency (IEA) states that in 2021, global sales of EVs (PHEVs and BEVs) doubled from their 2020 level to reach 6.6 million vehicles. 53% of worldwide sales, or around 3.4 million vehicles, were made in China, followed by Europe (33% of global sales), and the US (11% of all sales). Moreover, in the year, sales of EVs accounted for 8.6% of all auto sales worldwide, a dramatic increase on the meagre 0.9% recorded in 2016. It is estimated that around the world, there are now some 16 million EVs in use.
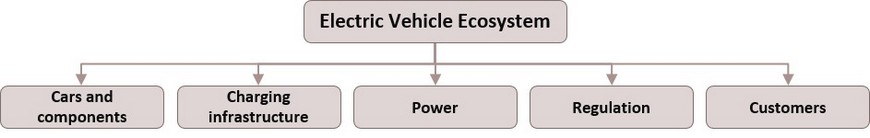
This rapidly strengthening demand is prompting the development of an accompanying ecosystem within the EV market. This is based on five principal components, these being production of the core EV parts (e.g., batteries and motors), public charging stations, electricity production, legal and regulatory frameworks, and consumer demand.
- Manufacturers of autos and the most important auto parts are now rushing to meet growing demand by developing and broadening the range of goods that they offer, with BloombergNEF[1] reporting that as of 2021, there were over 500 PHEV and BEV models on offer. This represents a 5-fold increase on the 2016 total, and it is expected that a further 180 models will be released to the market over the next 2 years. Major auto companies are also partnering with battery manufacturers to extend EV technology, and this is steadily increasing the efficiency and potential of these vehicles; between 2016 and 2021, the average range of newly released models climbed from 233 to 350 kilometers, an increase of 50.2%.
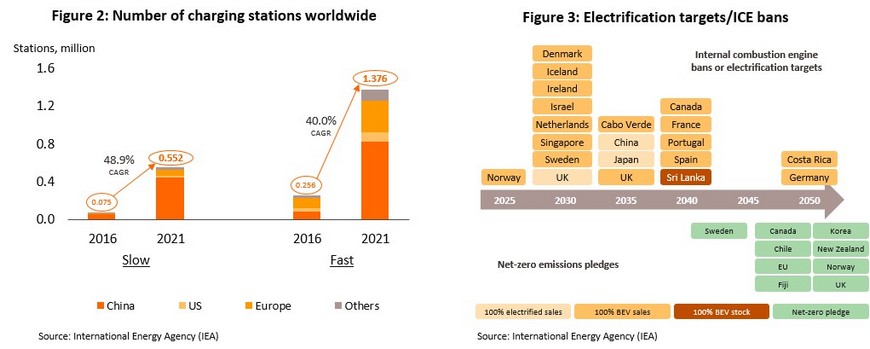
- The number of charging stations available worldwide is rising, and the IEA reports that there were 1.93 million of these in operation in 2021, split between 1.38 million slow-charge stations (up 50% from 2020) and 0.55 million high-speed charging stations (up 43% from 2020), although it should be noted that over 65% of these are in China (Figure 2). Considered with regard to the number of EVs on the road, in 2021, there were 1.2 charging stations for every 10 EVs worldwide, higher than the EU recommended ratio of 1 station to every 10 vehicles[2]. However, although the rising number of charging stations indicates that EV infrastructure is ready to support stronger demand, the distribution of these rather than just their sheer number remains an important factor that will determine worldwide rates of EV uptake.
- Many countries have adopted ambitious plans to accelerate EV adoption rates, with Norway, Denmark, Iceland, Singapore, and the UK each setting out plans to ensure that before 2030, 100% of new vehicle sales are of EVs, while China and Japan have the same goal for 2035. In pursuit of these targets, national governments have put in place a range of financial and non-financial incentives. Thus, in France and Germany, subsidies of around USD 7,000 are being made available for purchases of EVs, while China is ensuring that the country is effectively covered by charging stations, as well as offering monetary and non-monetary enticements to buyers of EVs[3].
In the case of Thailand, however, EVs have not achieved significant market penetration. This is for a variety of reasons, including their high price, a lack of clarity over the assistance offered to the segment by the government, a lack of supporting infrastructure, and the limited range of models on sale in the country. If Thailand were simply an importer of autos for consumption on the domestic market, this might not matter, but the country is home to a globally important auto industry and if Thailand-based manufacturers are to maintain their competitiveness and so allow the country to sustain its position as a world-leading player in the auto sector, it is imperative that the domestic market adapts to changes that are happening at the international level. Krungsri Research thus believes that it is essential that interested parties gain a better understanding of the EV ecosystem, in particular of the nature of rapidly strengthening consumer demand. This will then allow players in the industry to better plan and adapt to future changes in the business environment.
The survey investigating future demand for EVs in Thailand
To better understand and prepare for future changes in the Thai market for EVs, Krungsri Research joined with Krungsri Auto to survey the opinions of general consumers regarding the factors likely to affect their future use of EVs. The survey was distributed online over the period 10-30 November 2021, and answers were gathered from 818 respondents.
General information
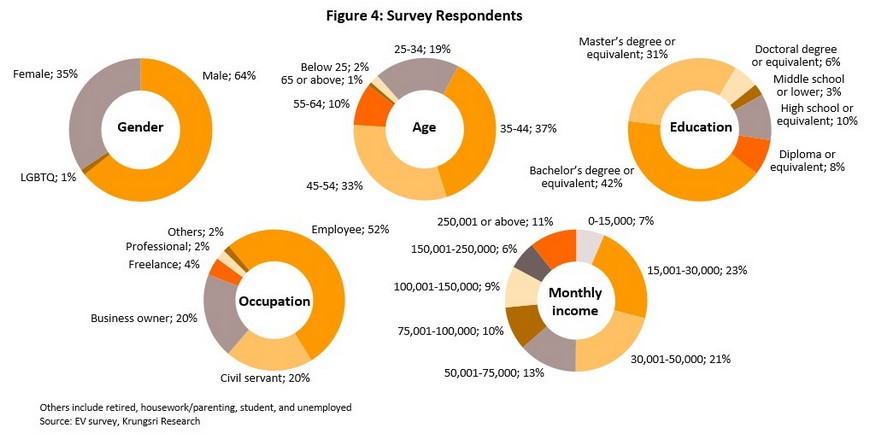
64% of respondents were male, and the overwhelming majority were aged 35-54 (37% were in the 35-44 age band and 33% were in the 45-54 age group). 42% had a bachelor’s degree and 31% had a master’s degree. 52% worked for a private-sector employer, 20% worked for the public sector, and another 20% were business owner. The majority of respondents were also in the middle-income group; 44% had a monthly income of THB 15,000-50,000 and 32% earned THB 50,000-150,000 per month.
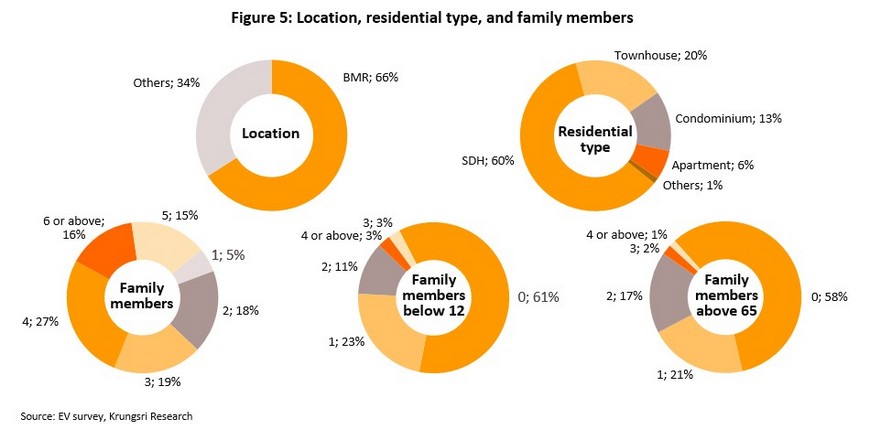
66% of survey respondents lived in the Bangkok Metropolitan Region. 60% lived in a detached house, 20% lived in a townhouse, and 13% lived in a condominium. Most commonly, respondents indicated that their family consisted of 4 members (including the respondent), though 61% of families did not contain a child aged below 12 and 58% did not live with an elderly member of the family.
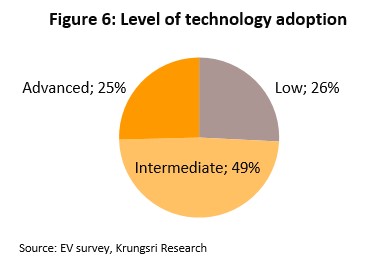
Rates of technological adoption were measured through respondents’ use of proxies that included mobile telephones, personal computers, robotic vacuum cleaners, dishwashers, smart watches, smart home systems, air purifiers, and electronic sterilizers. 49% of respondents were found to show an intermediate level of technological adoption, 26% were at a low level, and 25% were at a high level.
Respondents’ travel habits
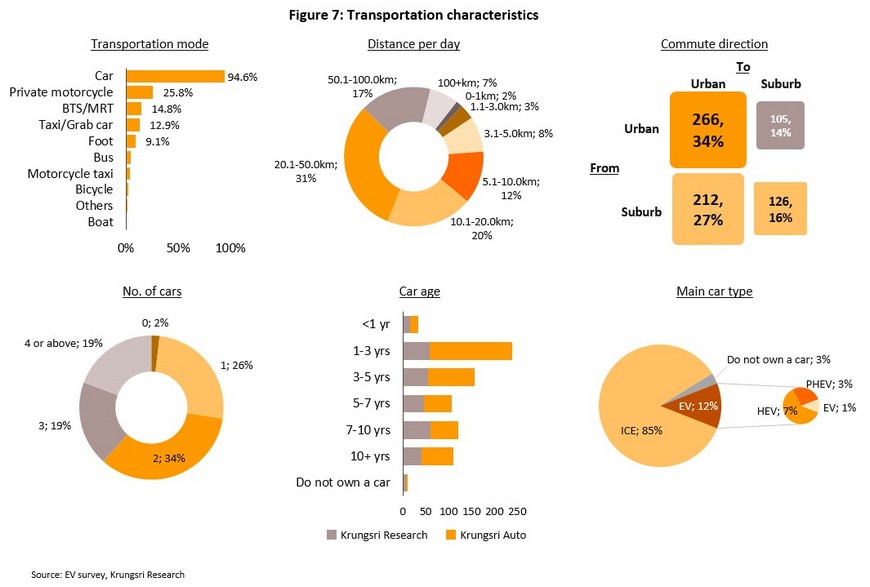
94.6% of respondents reported using their own car to travel, 25.8% used their own motorcycle, and 14.8% used the BTS/MRT networks. 31% of all respondents travelled 20-50 kilometers per day, with only 16% regularly travelling outside the main city area.
Around a third of respondents lived in family units that owned 2 vehicles, while 26% had only a single vehicle. A plurality of respondents (31%) reported owning vehicles 1-3 years old4/, and 85% used an ICE-powered auto as their only or main vehicle. A further 12% used an EV, with 7% using an HEV, 3% using a PHEV and 1% using a BEV.
Respondents who already drove an EV
For current EV owners or users, the 3 most commonly cited reasons for purchasing an EV were its lower running costs (81%), reduced environmental impacts (73%), and technological appeal (59%). However, branding and non-financial benefits (e.g., access to special EV parking facilities) did not appear to influence purchasing decisions.
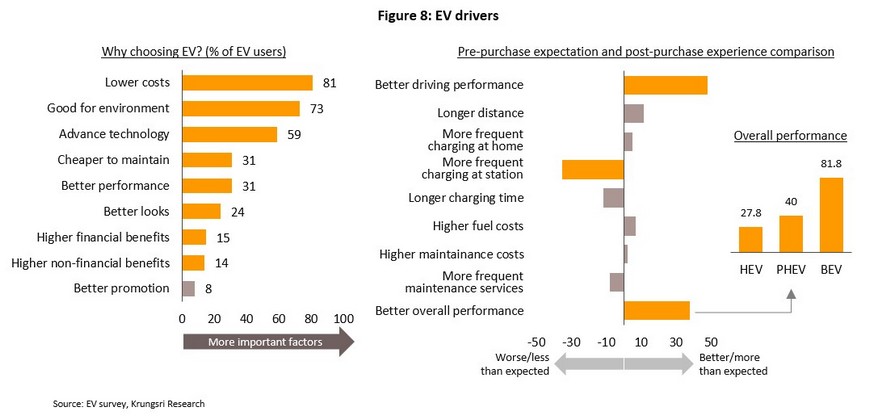
The majority of EV drivers reported that their driving experience with an EV was better than expected, that they had to make fewer visits to a charging station than anticipated and that overall, they were more satisfied with their EV than they had predicted. This was especially the case for drivers of BEVs, with 81.8% reporting that the experience was better than expected. Owners of BEVs also planned to drive their vehicles faster and further, though to do so in a more economical way (e.g., by driving at 80 kph, which is the most economical speed at which to drive).
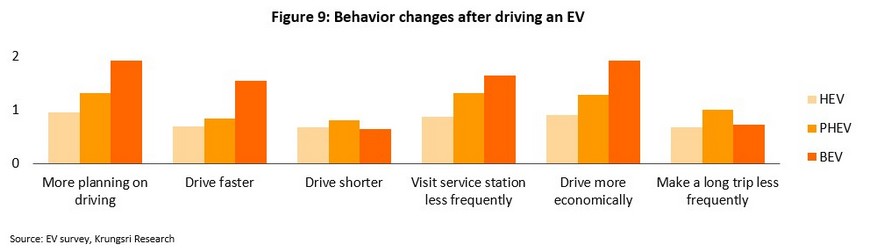
Nevertheless, respondents still reported problems with EVs, especially with charging, for example, with the slow charging speeds and the lack of charging stations. Respondents also reported feeling that the EVs’ range per charge was still too low.
Respondents who had not yet used an EV
For respondents who had not yet bought an EV, the most commonly given reasons were related to charging. The most important factors tipping these individuals towards not buying was the limited number of charging stations, EVs low range, the high cost of EVs relative to ICE-powered vehicles, and slow charging speeds. However, branding and technological limitations had little impact on the self-reported reasons for not buying an EV. Intriguingly, non-owners of EVs were most interested in BEVs, potentially indicating that from the demand side, in the future the Thai market may jump directly from ICE vehicles to BEVs, skipping over both types of intermediate hybrids.
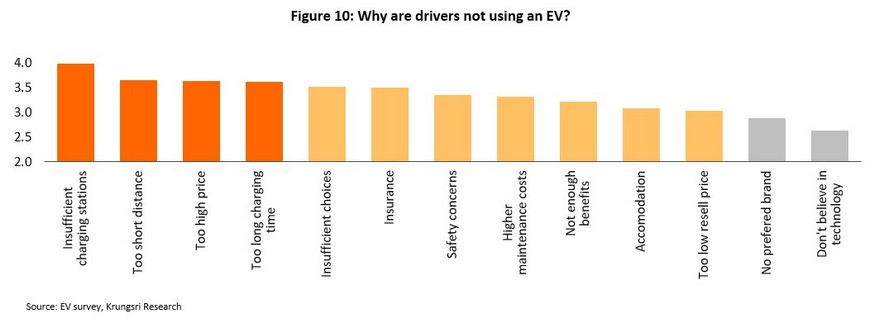
Asking generally about opinions on EVs, most non-owners were relatively ignorant about these but if they received more information, respondents were generally most interested in BEVs. Despite this, most believed that EVs had fewer negative impacts on the environment than ICE-powered vehicles, while 73.7% of non-owners also believed that the current range of EVs was sufficient for normal use and over 80% believed that EVs performed better than ICE vehicles. The main obstacles in the way to greater acceptance of EVs in Thailand are thus likely to revolve around a lack of knowledge of EVs and their relatively high price. On the other hand, worries related to charging can be expected to lessen when consumers actually try out EVs for themselves.

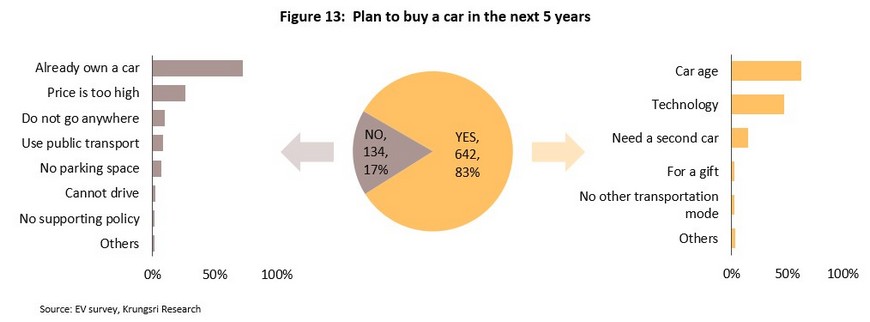
Plan to buy a car over the next 5 years
83% of respondents expected to buy a vehicle within the next 5 years, with the most important reasons for this being (i) the age of their current vehicle, and (ii) a desire to upgrade their vehicle in line with new technology. The 17% of survey respondents who did not expect to buy an EV over the next 5 years reported that this was because their vehicle was not old enough to need replacing and that EVs were too expensive.
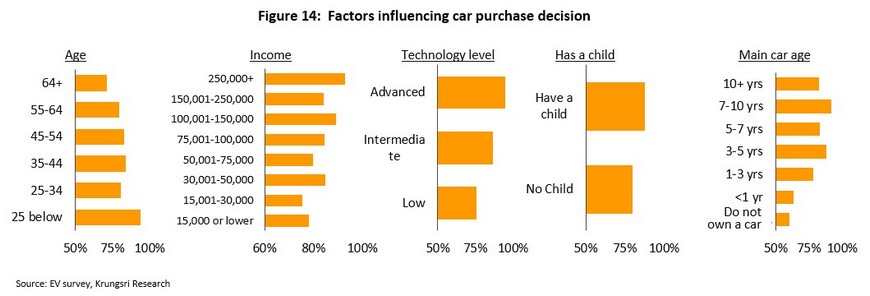
Our research shows that the decision to replace a vehicle over the next 5 years is most strongly influenced by the age of the respondent, their income, their level of technology adoption, being a parent, and the age of their current vehicle. Thus, younger individuals who earn more, show higher levels of interest in technology and who are parents report an above average intent to buy an EV. More generally, car owners also appear to change their vehicles on 3-5- or 7-10-year timescales.
Future demand for EVs
The survey results indicate that domestic demand for EVs will begin to build over the next 1-2 years, with this spreading into the consumer mainstream in around 3 years’ time. Demand growth will be accelerated by an increase in the number of charging stations, lower charging times, and better guarantees for batteries. However, non-monetary benefits such as access to parking spaces that are reserved for EVs, and branding are not expected to have a significant effect on purchasing decisions.
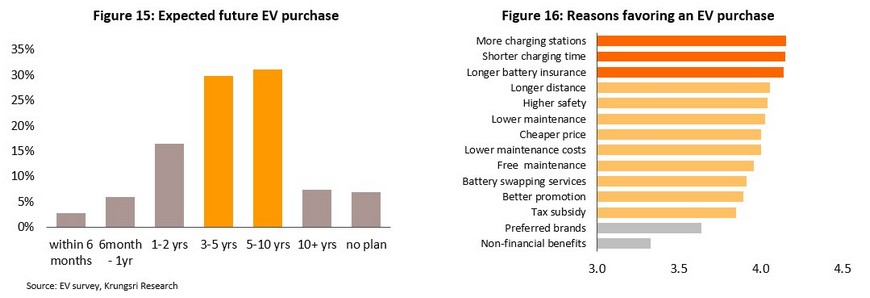
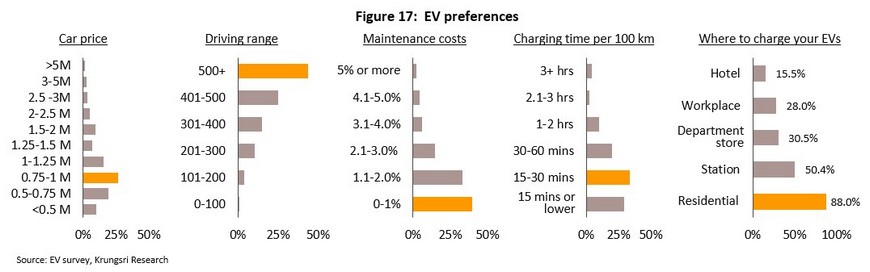
Respondents were most interested in smaller EVs priced in the THB 0.75-1.0 million band that had a range in excess of 500 kilometers, service costs below 1% of the ticket price, and charging times of 15-30 minutes per 100 kilometers. 88% of those surveyed expected to charge their EV at home, 50.4% thought they would do so at a service station, and 30.5% anticipated using department-store charging stations.
Factors affecting the decision to buy an EV
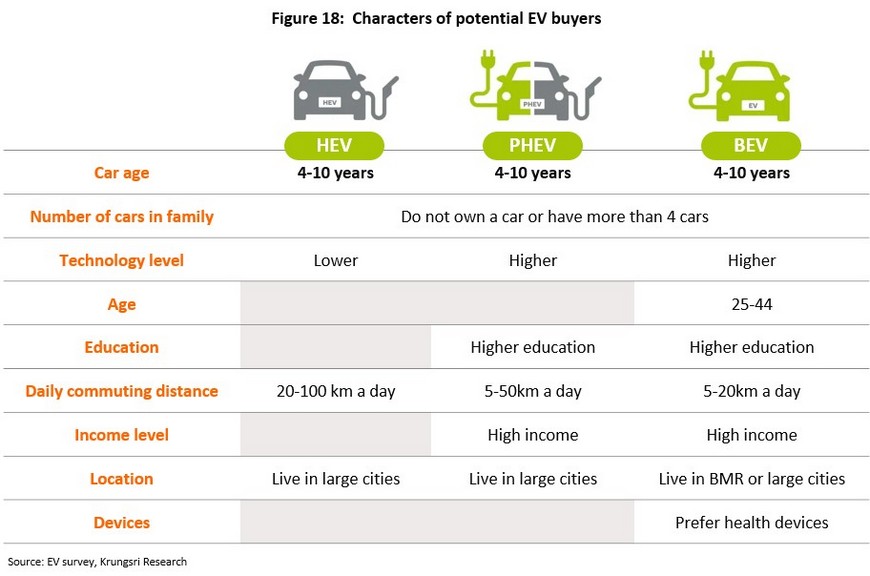
Nine factors emerged as having an impact on the decision to buy an EV. These were: (i) the age of the respondent’s current vehicle; (ii) the number of vehicles currently owned by the respondent’s family; (iii) the respondent’s level of technology adoption; (iv) the respondent’s age; (v) the respondent’s education; (vi) the average distance travelled daily by the respondent; (vii) the respondent’s income; (viii) the respondent’s place of residence; and (ix) the respondent’s possessions.
Econometric analysis shows that the age of the current vehicle and the number of vehicles owned by the respondent’s family are common factors affecting the intention to buy an EV. In this case, expressing a stronger than average intention to buy a new EV was linked to the desire to change the current main vehicle every 4-10 years and either not having any vehicles in the family or having 4 or more.
In addition, increases in education, technology adoption, and income were all positively correlated with a strengthening intention to purchase a BEV or a PHEV. For BEVs alone, interest was also strongest for those aged 25-44, those who were interested in personal health, and those who travelled 5-20 kilometers per day, which was shorter than the typical daily journey made by those interested in PHEVs and HEVs. Living in the Bangkok Metropolitan Region or another large urban area was also linked to a greater interest in purchasing an EV.
Krungsri Research view
The results of the survey with regard to likely future demand for EVs in Thailand, taken together with the growing interest in EVs globally, points to the importance of establishing a supporting ecosystem that encompasses all parts of the EV industry, running for example from development of EVs and batteries, through government assistance for the industry, to expanding the build out of charging stations. This will then help to reduce obstacles on the supply side of the market and so speed up adoption of EVs over the next few years. Indeed, Krungsri Research believes that the electrification of personal transport systems is likely to unfold more rapidly than many expect, and this will in turn likely generate significant turbulence in the auto market, with major consequences for auto manufacturers and players in associated industries. Given this, it is even more important that these changes are made.
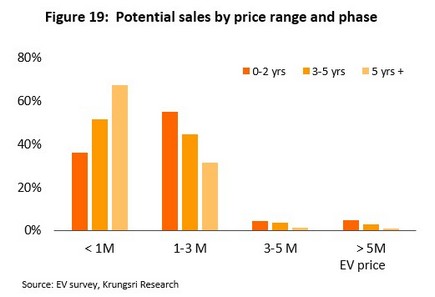
Domestic demand for EVs will strengthen significantly over the next 3 years. At first this will tend to be concentrated
at the more expensive end of the market but with time, demand will spread to more moderately priced models.
The survey results indicate that domestic demand for EVs will begin to be felt in 1-2 years. At first, this will be concentrated at the mid to upper end of the market but following this initial phase, demand will rapidly build, in particular below 1.0 million (Figure 19). The likely evolution of domestic demand as revealed by this analysis is described below.
In the coming period, demand for EVs in Thailand will undergo a substantial change and the market will be transformed by shifts in the consumer groups that are most prominent, this then having knock on effects for the types of vehicles that are most popular. In light of this, auto manufacturers and those offering related services will need to look for new ways of best meeting demand originating from these varied consumer segments.
Drivers typically view EVs as being a new kind of product and because of this,
brand loyalty may be significantly lower than manufacturers and service providers expect.
Krungsri Research’s findings show that when considering purchasing a new EV, buyers have a marked tendency to choose vehicles made by manufacturers other than that of the buyer’s current vehicle. Indeed, when individuals bought a new EV, only 28% of buyers purchased an EV that bore the same marque as their current vehicle. A full 72% of purchases were for vehicles made by a different company, of which 13% of purchases were for EVs made by new entrants to the market that had never manufactured an ICE-powered vehicle. In light of this weakening of brand loyalty, auto manufacturers that are slow to adapt to what is a rapidly evolving environment run the risk of seeing their market share shrink in the near future.
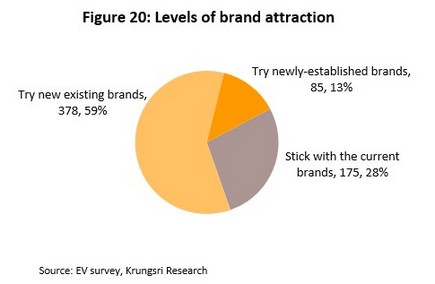
The drop in brand loyalty seen when purchasing an EV indicates that consumers potentially view EVs as being in a different category to their existing vehicle, and as such, the benefits that they are looking for in a vehicle and in related services are likely to change, too. In this environment, although existing manufacturers will continue to have an advantage over new entrants to the market with regard to their brand recognition, the ability to be nimble-footed in adjusting to changing consumer needs will be an extremely important factor in deciding which players are able to preserve their competitiveness as time goes by.
Charging and the provision of charging stations remains an obstacle to greater take-up of EVs in Thailand,
but this is also opening new business opportunities across several industries.
The results of the survey show that in Thailand, both current owners of EVs and those who have yet to buy one believe that the current low supply of charging stations and EVs’ extended charging time pose significant obstacles to buying and running an EV. Nevertheless, the majority of respondents who already owned an EV reported having to use a charging station less often than expected, while 73% of those who do not yet own one believe that the average range of EVs is sufficient for normal use and so a full 88% of these respondents said that if they did buy an EV, they would mostly charge it at home. It is therefore likely that for the vast majority of users, it will be possible to use an EV just like any ICE car during the day and then to return home and recharge it overnight. This will largely remove the need to use charging stations, overcoming perceived problems with a lack of these and the lengthy charging process, and if consumers become more aware of this fact, this would help to alleviate fears around this issue. One way of approaching this problem may be to expand access to EV rentals since this would help to increase general familiarity with EVs and to reduce fears about potential problems with charging before buyers are in the position of making a purchasing decision.
The majority of owners expect to charge their vehicles at home, and this is paving the way to new business opportunities. These include manufacturing and installing home charging stations, and servicing and repairing these (in both condominiums and houses) as well as related activities, such as producing equipment for solar power generation and the manufacture of energy storage devices.
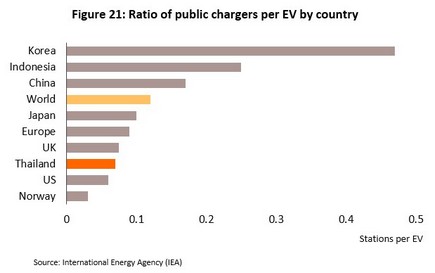
Nevertheless, it remains true that having the option of charging EVs at public charging stations helps to build confidence among current and potential owners, and so increasing access to these in urban and rural areas forms an important part of moves to increase acceptance of EVs. As stated above, the EU recommends a minimum of 0.1 charging points per electric vehicle on the road, but unfortunately, the ratio in Thailand is only 0.07 so it is important that the total number of charging stations is increased. However, the location of charging points is at least equal in importance to their raw number, and in some countries that have achieved somewhat high EV penetration rates, such as Norway and Iceland, the number of charging points is very low relative to the total number of EVs being driven. Indeed, in these two countries, there are just 0.03 points per EV, but this low rate is compensated for by their location and ease of access, as well as by the high proportion of high-speed chargers (i.e., those rated at over 20 kW). Thus, access to charging points and supporting infrastructure and the type of charging stations are all factors that influence the success of EV service stations, which in turn helps to widen the use of EVs more generally.
Industries are becoming more interconnected and integrated,
and this is creating both opportunities and challenges in the EV industry and related areas.
Rising demand for EVs and changing consumer needs are adding to the pressure experienced by players in the auto sector, and in the future, this is certain to result in dramatic changes to supply chains and the types of goods and services provided to the market, though it will also lead to new linkages between players both inside and external to the industry. As boundaries between different business activities and indeed between different industries increasingly mutate, shift and overlap, it will become easier for players to slip between industries, as seen recently in the growing trend for tech companies to move into auto production. This will then add to the competitive pressure within these industries and pile on the challenges faced by incumbent players, who will thus have no option but to sharpen their competitiveness if they wish to remain active and relevant against a background of rapid and fundamental change. With the traditional business landscape undergoing this breathless transformation, Krungsri Research believes that players will need to raise their game by forging new alliances and building new supply chains, some examples of which are given below.
- Building supply chains linking EV manufacturers and producers of batteries and other major components: Across all their major parts, from the motor to the transmission and the exhaust system, EVs are generally built from far fewer components than ICE vehicles and so if EVs become much more popular, the structure of auto industry supply chains will be fundamentally transformed. That said, although EVs use fewer parts, each part (e.g., batteries, motors, inverters, etc.) will assume a correspondingly greater importance, and both lower costs and technical progress in their design and operation will have important consequences for EV production. Increasing cooperation and developing partnerships between auto assemblers and manufacturers of the major parts will therefore help existing players maintain their competitiveness.
- Developing partnerships between EV manufacturers and auto rental operations/car sharing services: Consumers remain somewhat hesitant to purchase EVs for two reasons: (i) most lack knowledge about EVs, and (ii) rapid technological progress means that buyers tend to see their EVs depreciate in value very quickly. Krungsri Research thus believes that working with car rental businesses could help to ease both fears over the use of EVs and problems with the excessively fast depreciation of secondhand vehicles. Partnering with car sharing enterprises could also help support stronger demand for EVs among those who do not need to own a vehicle outright, which is especially the case for younger drivers.
- Developing partnerships between EV manufacturers and manufacturers of home charging equipment: Because the majority of the respondents to the survey indicated that if they owned an EV, they expected to charge it at home, and charging times have an important influence on the decision to purchase, manufacturers will be able to increase their competitiveness if they are able to provide buyers with an efficient home charger.
- Developing partnerships between manufacturers of EV home chargers and producers of solar rooftop installations and energy storage systems: Rooftop solar and associated battery systems are falling in price all the time, making it increasingly attractive to use these to power private home-based EVs. In addition, it is possible to sell any surplus electricity generated by the solar installation into the national grid, making the investment even better value.
- Developing partnerships between service stations, retailers and restaurants: Because more EV service stations are needed and charging times remain rather lengthy, greater cooperation between forecourt owners, retailers and restaurants will help to attract more customers.
Risks to the auto industry as EVs achieve greater market penetration
Depreciation in vehicle values will have a direct impact on the risk assessment of auto hire-purchase and leasing companies. Analysis by Moody’s Analytics and the European Consumer Organization shows that at first, EVs will depreciate in value faster than ICE-powered vehicles since the former are still at an early stage of development, and because the technology deployed in these is undergoing constant and rapid improvement, consumers have a natural preference for new vehicles, rather than secondhand EVs and the older, outdated technology that these rely on. However, as the EV market develops and core technologies mature and stabilize, the impact of technological progress on secondhand prices will decline in importance, while because EVs have fewer parts and experience less wear and tear, they will likely depreciate even slower. In addition, demand for ICE-powered vehicles is likely to weaken with time, further eroding their secondhand value. In light of this, auto leasing and hire-purchase companies together with auto insurers will need to be alert to the rising risks entailed in valuing EVs and ICE vehicles, especially as use of EVs picks up in the future.
The global auto industry is entering a period of huge transformations. Electrification of powertrain, autonomous driving, and the servicification of the mobility sector are having deep impacts across the industry, and not just on auto manufacturers themselves but also on parts manufacturers, dealers, retailers, service stations, and connected parts of the economy including banking, insurance and the public sector. The metamorphosis of the industry that this is driving will add to the challenges faced by players, which are also dealing with rising competitive pressures, but shifting their stance and adapting to these changes will not only allow companies to retain their competitiveness, but it will also put them in a position to seize rapidly emerging opportunities as the new automotive era comes of age. On the demand side, although at first, many obstacles will lie in the way of progress, overcoming these will help to bring forward mass acceptance of EVs, possibly significantly ahead of the schedule anticipated by many parties, and so while players in the auto sector that make the leap of faith into the EV segment will have to contend with significant risk, they may well be rewarded with a commanding market share. The converse of this is that players that dither and hesitate in the face of these newly emerging challenges run the risk of missing out on major business opportunities. Thus, as always, fortune favors the brave, and it will only be players that are swift to change their business orientation that will be able to take advantage of what are potentially huge future opportunities in the EV market.
[1] Electric Vehicle Outlook 2021, BloombergNEF (June 2021)
[2] .From the European Union’s Alternative Fuel Infrastructure Directive (AFID), which gives directions on policy related to alternative energy and the auto sector.
[3] Global EV Outlook 2021, International Energy Agency
[4] Because most respondents were customers of Krungsri Auto, the information available to Krungsri Research indicated that the typical ages of the principal vehicle(s) used by respondents were similar across all age groups.